Choosing the right twist drill bit for your project involves understanding three key factors: material, coating, and geometric features. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in the performance and durability of the drill bit. Here's a closer look at how to make an informed decision.
Material
1. High-Speed Steel (HSS):
High-Speed Steel (HSS) has been integral in cutting tools for over a century, valued for its wide application and affordability. HSS drill bits are known for their versatility, performing well with both hand drills and stable platforms like drill presses. A key advantage of HSS is its re-sharpening capability, enhancing the longevity of drill bits and making it a cost-effective choice for lathe tools as well. Furthermore, HSS has different grades, each with different elemental compositions to cater to specific cutting needs. This variety in steel grades adds to the adaptability of HSS, making it a versatile and essential component in diverse machining tasks.
2. Cobalt HSS (HSSE or HSSCO):
Compared to traditional HSS, Cobalt HSS shows superior hardness and heat endurance. This enhancement in properties leads to significantly improved abrasion resistance, making HSSE drill bits more durable and efficient. The incorporation of cobalt in HSSE not only contributes to its increased abrasion resistance but also enhances its overall lifespan. Much like standard HSS, HSSE bits retain the benefit of being re-sharpenable, which further extends their usable life. The presence of cobalt in HSSE makes these bits especially suitable for more demanding drilling tasks where durability and resistance to abrase are essential.
3. Carbide:
Carbide is a metal matrix composite, primarily made of tungsten carbide with various binders. It significantly surpasses HSS in hardness, heat endurance, and abrasion resistance. While more expensive, carbide tools excel in lifespan and machining speed. They require specialized equipment for re-sharpening.
Coating
Drill bit coatings vary widely and are chosen based on the application. Here's a brief overview for some common coatings:
1. Uncoated (Bright):
It’s the most common color for HSS drill bits. Ideal for soft materials like aluminum alloys and low carbon steel, uncoated tools are the most affordable.
2. Black Oxide Coating:
Provides better lubrication and heat resistance than uncoated tools, improving lifespan by over 50%.
3. Titanium Nitride (TiN) Coating:
Titanium-coated drill bits perform well in many application scenarios due to their unique performance characteristics. First, It enhances hardness and abrasion resistance through the coating, allowing the bit to stay sharp while drilling through harder materials, and providing a longer service life. These bits reduce friction and heat buildup, increasing cutting efficiency while protecting the bit from overheating. Titanium-plated bits are suitable for use in many materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum and wood, making them ideal for engineering and household applications. In addition, these bits penetrate materials faster and cleaner, providing a neater cutting surface. While titanium-plated drills may cost more than regular drills, their high efficiency and long life make them a good return on investment for applications that require high abrasion resistance and precise cutting.

4. Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) Coating:
First, AlTiN coatings are extremely heat resistant, enabling them to excel in high-speed cutting and machining of high-temperature alloys. Secondly, this coating significantly improves the abrasion resistance and extends tool life, especially when machining hard materials such as stainless steel, titanium alloys and nickel-based alloys. In addition, the AlTiN coating reduces friction between the drill bit and the workpiece, improving machining efficiency and helping to achieve a smoother cutting surface. It also has good oxidation resistance and chemical stability, enabling it to maintain performance in harsh working environments. In all, AlTiN-coated drills are ideal for high-speed, high-precision machining applications, and are especially suited to handling hard materials that pose a challenge to conventional drills.
Geometric Features
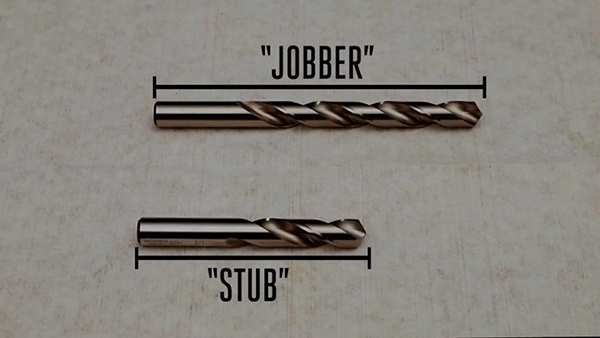
1. Length:
The ratio of length to diameter impacts rigidity. Choosing a drill bit with just enough flute length for chip evacuation and minimal overhang can enhance rigidity and tool life. Insufficient flute length may damage the bit. There are various length standards to choose in the market. Some common lengths are Jobber, stubby, DIN 340, DIN 338, etc.
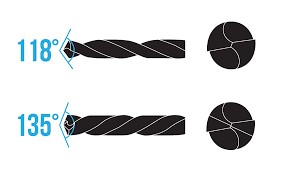
2. Drill Point Angle:
The 118° point angle is common for soft metals like low carbon steel and aluminum. It typically lacks self-centering capability, needs a pilot hole. The 135° point angle, with its self-centering feature, eliminates the need for a separate centering hole, saving significant time.
In conclusion, selecting the right twist drill bit involves balancing the requirements of the material being drilled, the desired lifespan and performance of the bit, and the specific requirements of your project. Understanding these factors will ensure you choose the most effective and efficient drill bit for your needs.
Post time: Jan-10-2024